Wait… there’s more than one type of data?! There absolutely is, and we’re here to break down each and which one to apply in your digital marketing strategy.
The quality and accuracy of data are paramount to crafting effective campaigns for Google ads, social media, email, and even content marketing.
The differences between various types of data—zero party, first party, second party, and third party—can significantly influence how brands understand and engage with their customers.
Let’s delve into these data types and explore why first-party data stands out as the most valuable for targeted and personalized marketing.
Let’s break all of this down so you can make the best decision for your campaigns and your clients.
What is Zero Party Data?
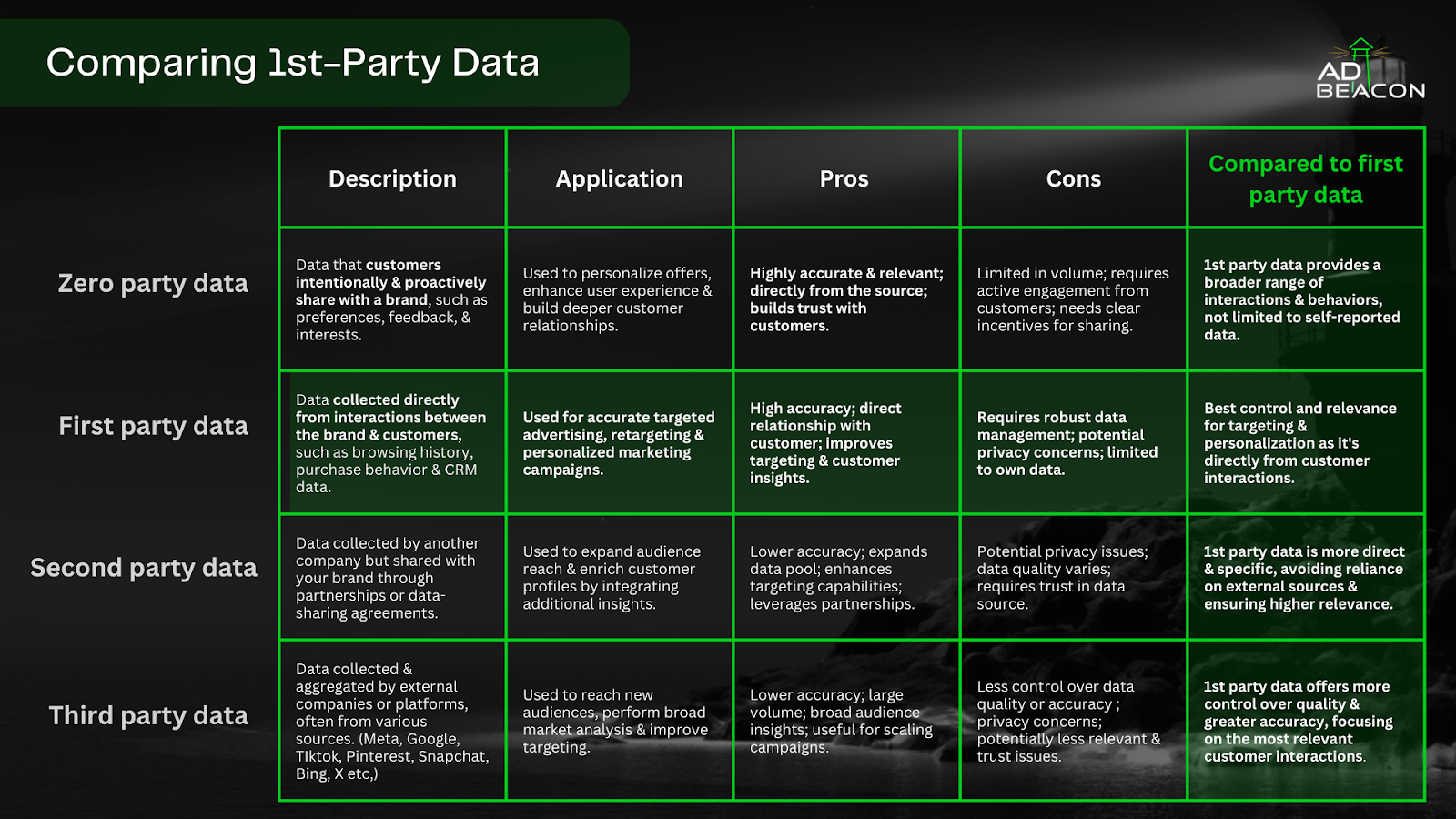
Zero party data is information that customers intentionally and proactively share with a brand. This includes preferences, feedback, and interests directly communicated by the customer.
For example, a customer fills out a survey on a clothing retailer’s website indicating their style preferences, favorite colors, and types of clothing they are interested in. This data is voluntarily provided by the customer to receive more personalized recommendations. This is a prime example of Zero-Party Data.
Application: This data type is primarily used to personalize offers, enhance the user experience, and build deeper customer relationships.
Pros:
- Highly accurate and relevant since it comes directly from the source.
- Builds trust with customers by respecting their voluntary disclosures.
Cons:
- Limited in volume and scope as it requires active engagement from customers.
- Necessitates clear incentives for customers to share this information.
Comparison to
First-Party Data
While zero party data is very accurate and trustworthy, first-party data provides a broader range of interactions and behaviors, offering more comprehensive insights beyond self-reported data.
What is First-Party Data?
First-party data is collected directly from interactions between the brand and its customers, such as browsing history, purchase behavior, and CRM data.
An e-commerce site tracks a user’s browsing behavior, noting which products are viewed, added to the cart, and ultimately purchased. This data is automatically collected through the user’s interactions with the site.
Application: It is used for accurate targeted advertising, retargeting, and personalized marketing campaigns.
Pros:
- High accuracy due to the direct relationship with the customer.
- Improves targeting and provides deep customer insights.
Cons:
- Requires robust data management systems.
- Potential privacy concerns due to the depth of data collected.
- Limited to the brand’s own data.
Why It’s Superior
First-party data offers the best control and relevance for targeting and personalization because it derives directly from customer interactions. This leads to more effective and efficient marketing strategies.
What is Second-Party Data?
Second-party data is collected by another company but shared with your brand through partnerships or data-sharing agreements.
To illustrate, consider this example. A fitness app partners with a nutrition company to share user data. The fitness app provides data on users’ exercise routines and goals, while the nutrition company shares dietary habits and preferences.
Both companies benefit from a more comprehensive understanding of their customers.
Application: This data helps expand audience reach and enrich customer profiles by integrating additional insights.
Pros:
- Expands the data pool and enhances targeting capabilities.
- Leverages partnerships for more comprehensive insights.
Cons:
- Lower accuracy compared to first-party data.
- Potential privacy issues and variable data quality.
- Requires trust in the data-sharing partner.
Comparison to
First-Party Data
First-party data is more direct and specific, avoiding reliance on external sources and ensuring higher relevance.
What is Third-Party Data?
Third-party data is collected and aggregated by external companies or platforms from various sources, including social media platforms and search engines.
This is the most prominent type of data ad platforms use everyday.
As another example: A digital marketing firm purchases data from a third-party provider that aggregates information from various online sources, such as social media interactions, search engine queries, and browsing history across multiple websites.
Application: It is used to reach new audiences, perform broad market analysis, and improve targeting for large-scale campaigns.
Pros:
- Large volume and broad audience insights.
- Useful for scaling campaigns and reaching new market segments.
Cons:
- Lower accuracy and less control over data quality.
- Significant privacy concerns and potential trust issues with the data source.
Comparison to
First-Party Data
First-party data offers more control over quality and accuracy, focusing on the most relevant customer interactions and ensuring more precise targeting.
Choose Your Data Wisely!
In the realm of digital marketing, the type of data you leverage can make a substantial difference in the effectiveness of your campaigns.
While zero, second, and third-party data have their uses, first-party data stands out for its accuracy, relevance, and control.
By focusing on data collected directly from customer interactions, brands can create more personalized and impactful marketing strategies.
AdBeacon specializes in harnessing the power of first-party data to optimize ad spend and enhance campaign performance. With AdBeacon’s advanced tools and insights, marketers can confidently navigate the complexities of digital advertising and achieve superior outcomes.
Embrace the power of first-party data with AdBeacon and transform your marketing strategies today.
If you haven’t experienced AdBeacon in action – you can click here to contact us and book your demo!